12/02/2022
Unequivocally, in order to choose the best heating system, various factors must be taken into consideration, including the type of home, i.e. whether it is a single house or an apartment, the area in which it is located, the annual temperature range , the energy sources available or usable, the structure of the house, for example regarding its thermal insulation, and finally the need to use the system.
Let us therefore analyze and compare the different types of heating systems proposed by the market today.
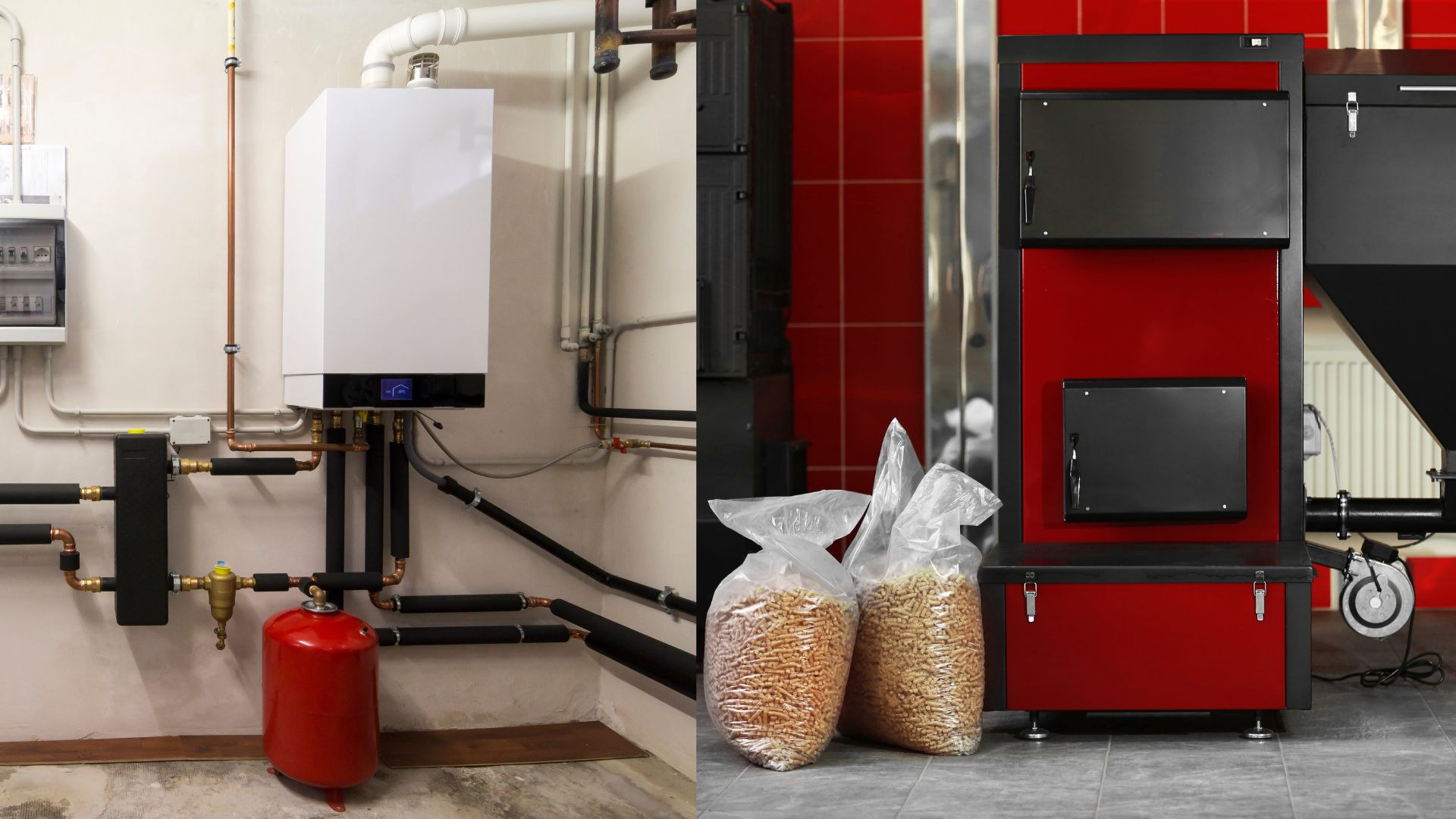
The boiler: condensation or biomass
The classic boiler combined with traditional radiators, as an alternative to a heating system, is certainly the most widespread in our homes. However, there are two different types of boiler systems most common today: condensing and biomass.
The condensing boiler is powered by gas and possibly accompanied by photovoltaic and radiant panels, which are renewable energies that allow you to save large percentages on the costs of the water heating bill. This heating system recovers energy from the condensation of the combustion fumes, guaranteeing excellent energy efficiency and low pollution.
Instead, the biomass boiler exploits the combustion of pellets, wood or wood chips, and turns out to be very interesting since it is able to heat the water that is circulated in the radiators and, therefore, that for sanitary use.

Fireplace and stoves
The stove, the traditional fireplace and the fireplace stove are excellent allies in the home, as they heat, remove humidity from the environment and allow, if desired, to cook some dishes in the traditional way. However, these solutions can only be an addition to the main heating supply, thus proving not to be excessively convenient either in terms of savings, much less in terms of practicality, especially with reference to wood, which requires great work and large spaces.

LPG cylinder and methane line
Most of the external tanks for heating homes are powered by methane and LPG, a gas obtained from a mixture of hydrocarbons. The heat yield of LPG and methane is almost the same; in economic terms, perhaps, methane proves to be more convenient, since it benefits from a distribution infrastructure.

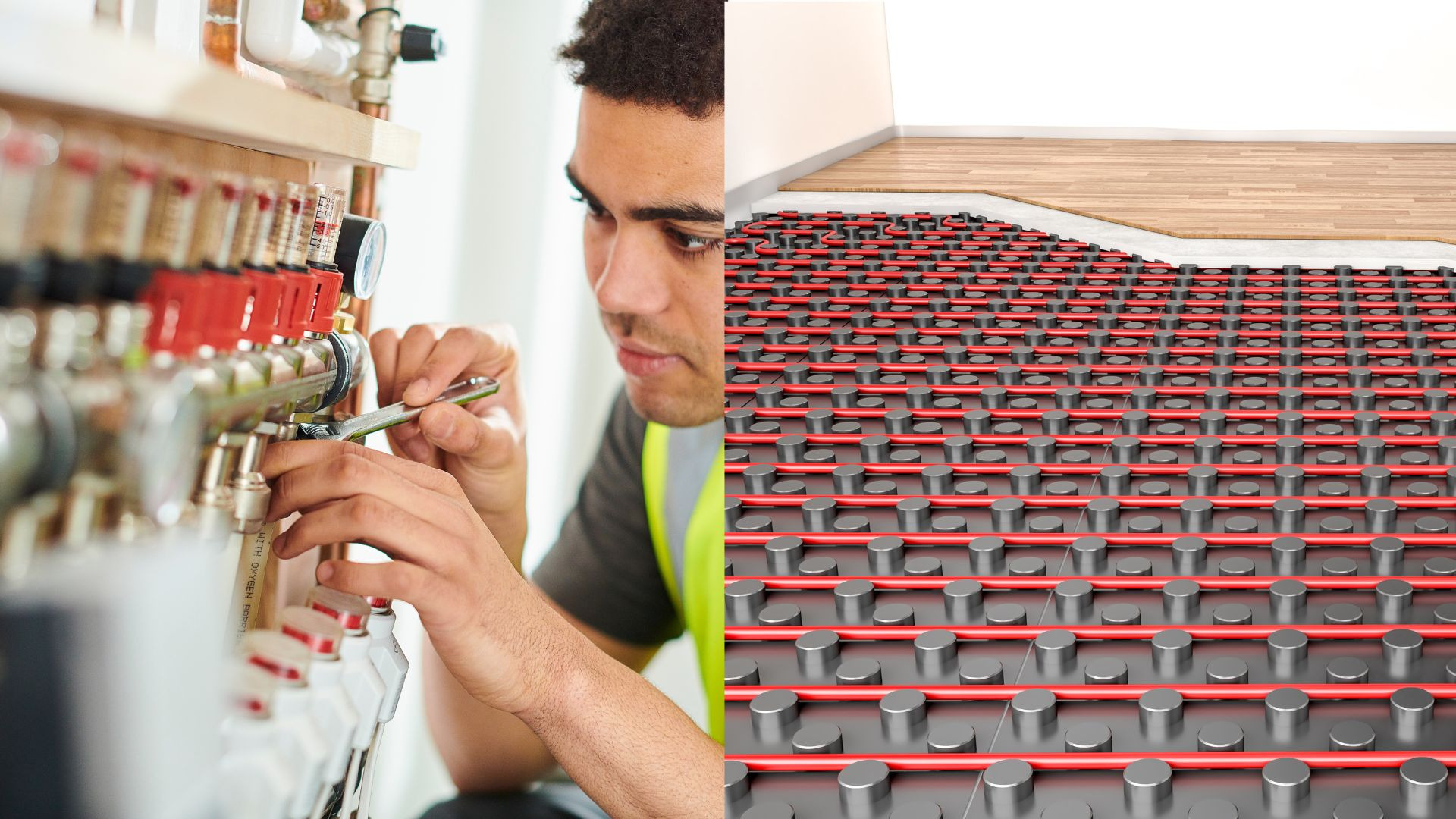
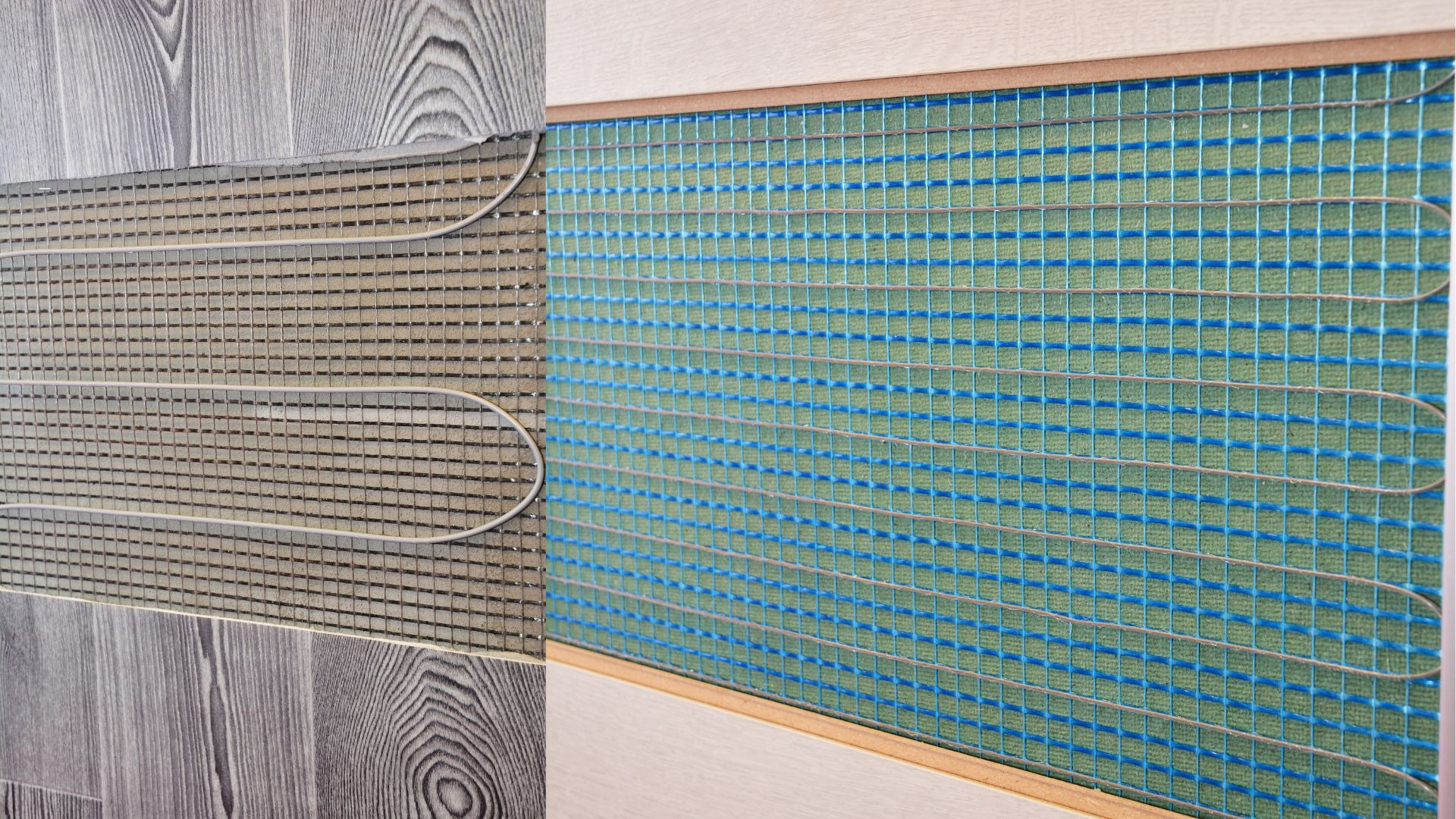
The underfloor system and the heat pump
The underfloor heating system is based on a system of radiant panels, placed under the cladding, which distribute the heat evenly over the entire surface of the house, guaranteeing greater maintenance of temperatures. The radiant floor therefore proves to be a valid solution to eliminate waste and integrates very well with the heat pump: installing one means making an important ecological and energy saving choice. The heat pump uses the thermal energy present in nature and, moreover, can be connected to a photovoltaic system, so as to produce electricity at no cost. The application of the heat pump, sees its savings from 40% to 60% more, compared to the consumption of the classic boiler.

The ceiling heating system
The ceiling heating system, like the underfloor one, is based on a radiant system, placed on the ceiling, i.e. the system is placed in a high percentage of the space in the house, thus having the advantage of spreading the heat evenly . Thanks to this system, surfaces absorb 90% of thermal radiation and radiate almost 100% of it!
The wall heating system
Like the two systems discussed above, the wall heating system is also a heat radiation system: the pipes pass behind the walls ensuring uniform heat and also a great aesthetic result.
The solar thermal system
Solar thermal heating is by far one of the best state-of-the-art heating systems. Thermal solar panels, to date, are increasingly replacing traditional boilers, both in terms of heating and hot water production.
